Amid the rapid expansion of Big Data, traditional storage models have increasingly revealed their limitations, giving way to more flexible data architectures such as Data Lake and Data Lakehouse. A clear understanding of the differences among these models is essential for enterprises to build an effective and sustainable data strategy.
Overview of data storage models
1. Data Warehouse – The foundation for traditional reporting and BI
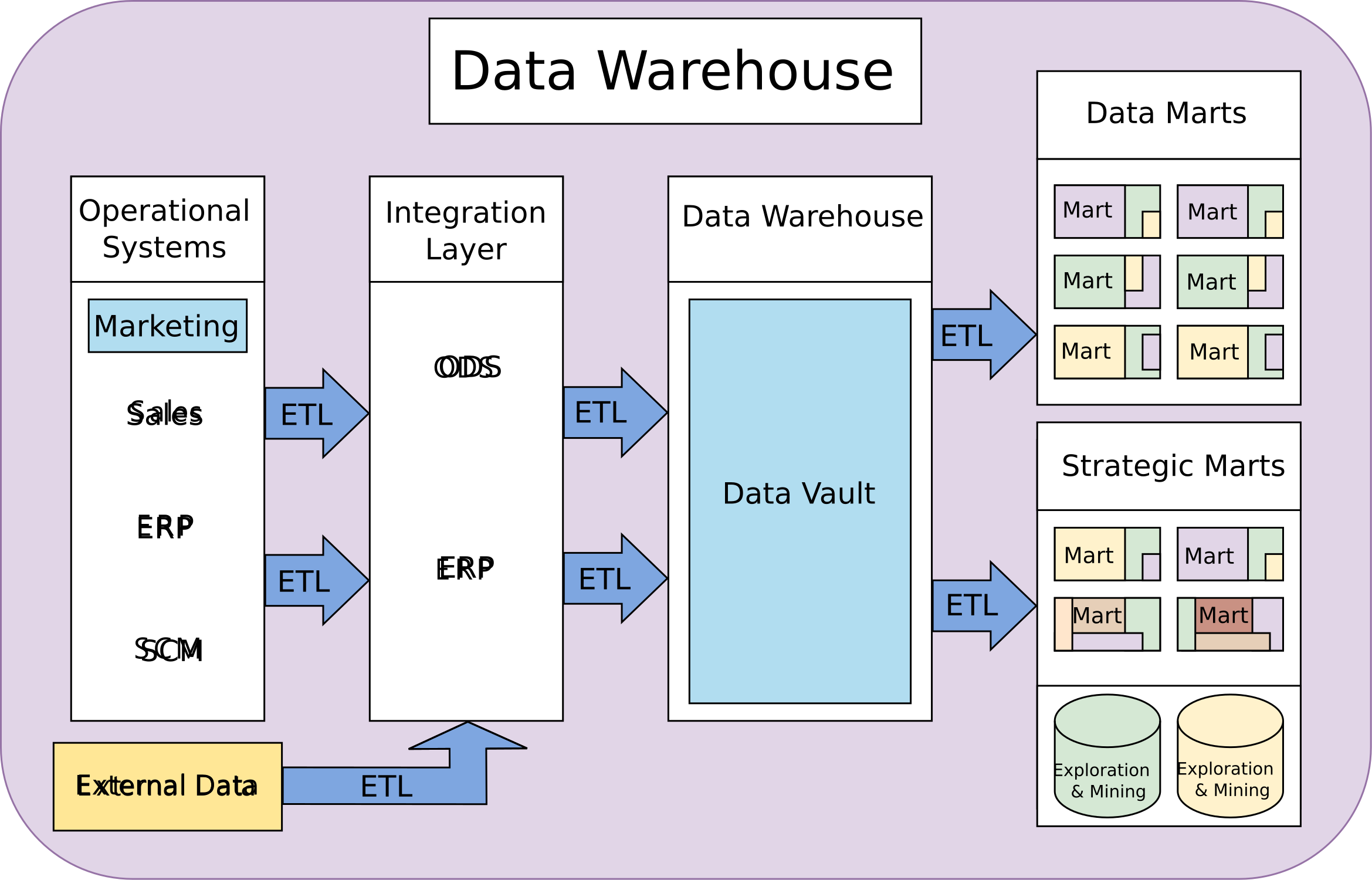
Data Warehouse Concept
A Data Warehouse is a structured data storage system in which data is cleansed and standardized before being ingested. This model is designed primarily to support analytics, reporting, and business intelligence.
Data is extracted from source systems (ERP, CRM, POS, etc.), then processed through ETL (Extract – Transform – Load) pipelines before storage. Only well-defined and structured data is loaded into the warehouse.
Advantages of Data Warehouse
- Consistent and reliable data, easy to analyze
- Well-suited for management reporting and KPI tracking
- High query performance
Limitations of Data Warehouse
- Limited flexibility when data structures change
- Inefficient for handling unstructured data
- High scaling costs as data volumes grow rapidly
2. Data Lake – A raw data repository for the Big Data era
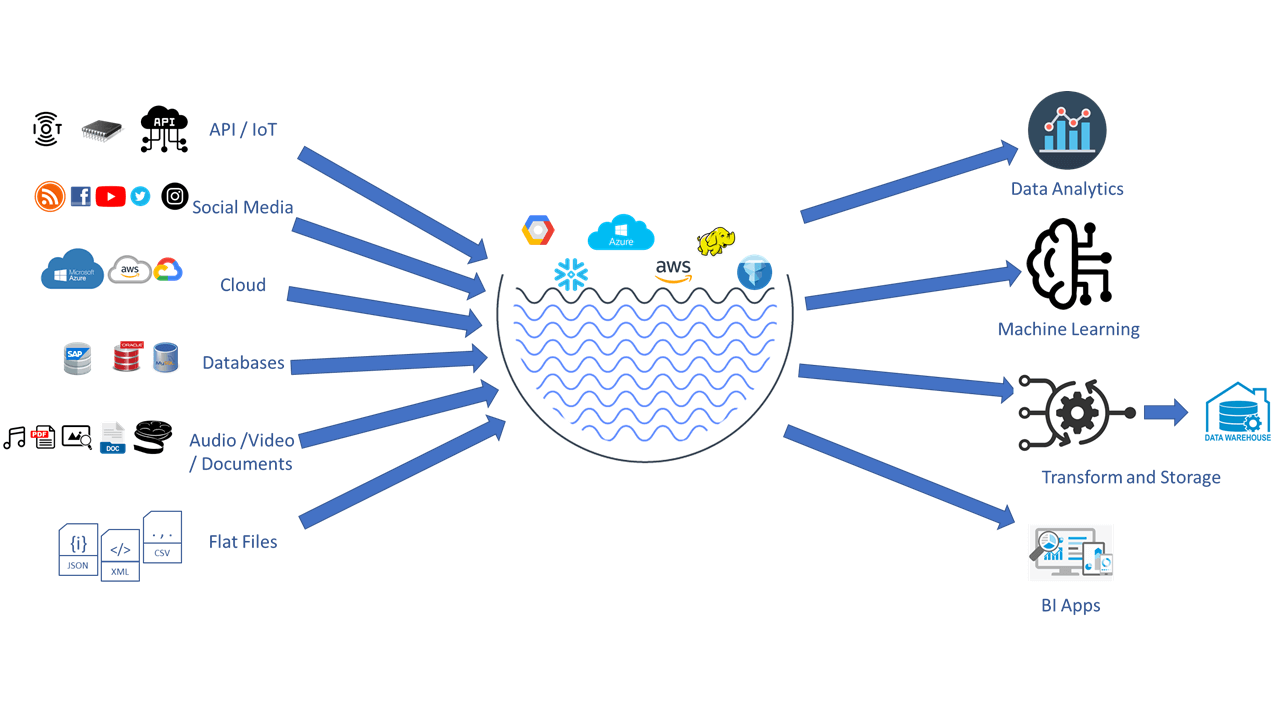
Data Lake Concept
A Data Lake is a storage model that retains data in its raw, native format, enabling the storage of all data types: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured.
Unlike Data Warehouses, Data Lakes adopt a schema-on-read approach, where data is stored first and structured later based on specific analytical needs.
Advantages of Data Lake
- Highly flexible storage with lower costs
- Well-suited for Big Data, AI, and Machine Learning workloads
- Easily scalable to accommodate rapid data growth
Limitations of Data Lake
- Prone to becoming a “data swamp” without proper governance
- Difficult to use with traditional BI tools
- Requires advanced data and technical expertise
3. Data Lakehouse – A next-generation hybrid data architecture
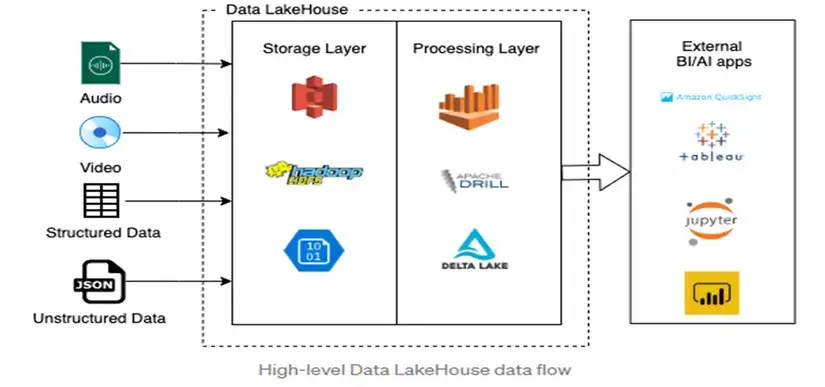
Data Lakehouse Concept
A Data Lakehouse combines the strengths of both Data Lake and Data Warehouse architectures, allowing organizations to store raw data while still enabling robust analytics, querying, and governance similar to traditional data warehouses.
Data is centrally stored on a Lake-based foundation while enhanced with governance layers, metadata management, indexing, and transaction support – enabling BI and AI workloads to run on the same unified system.
Value Delivered
- A single platform supporting both BI and AI
- Reduced operational costs by eliminating parallel systems
- Flexibility combined with strong data governance and control
Data governance complexity – A practical challenge for enterprises
As data becomes increasingly diverse and continuously generated, operating multiple storage systems in parallel exposes enterprises to several challenges:
- Rising infrastructure costs
- Fragmented data with no single source of truth
- Difficulty in delivering data-driven decisions quickly
- Heavy reliance on technical teams
Enterprises no longer need just a place to store data – they require a unified data platform that is easy to govern, manage, and exploit.
FPT Data Platform on FPT Data Suite – A comprehensive data platform for enterprises
FPT Data Platform on FPT Data Suite is designed with a modern Lakehouse mindset, enabling enterprises to:
- Flexibly store all types of data
- Centralize data standardization, governance, and security
- Simultaneously support BI, advanced analytics, and AI
- Operationalize data, not merely store it
Instead of choosing between a Data Lake and a Data Warehouse, enterprises can consolidate their data on a single platform—reducing complexity and accelerating decision-making.
Experience FPT Data Platform on FPT Data Suite: https://www.datasuite.vn/



